Think of your password as the key to your digital front door. It’s a decent first line of defense, but what if someone swipes it? Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is like adding a friendly but firm security guard who asks for a second form of ID before letting you in.
It's a security method that requires at least two separate pieces of evidence to prove you are who you claim to be, moving well beyond just a simple password. Think of it as your digital bouncer, making sure only the right people get past the velvet rope.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
Let's break that down in a friendly way. A password alone is like shouting a secret code from across the street—anyone who overhears it can get in. MFA, on the other hand, demands you prove your identity in multiple, distinct ways. This creates layers of security that are exponentially harder for an intruder to breach.
This layered approach is absolutely critical in any modern environment. Whether it's a school in the Education sector, a bustling shop in Retail, or a corporate office with a Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policy, you simply have to ensure that only the right people are accessing your network.
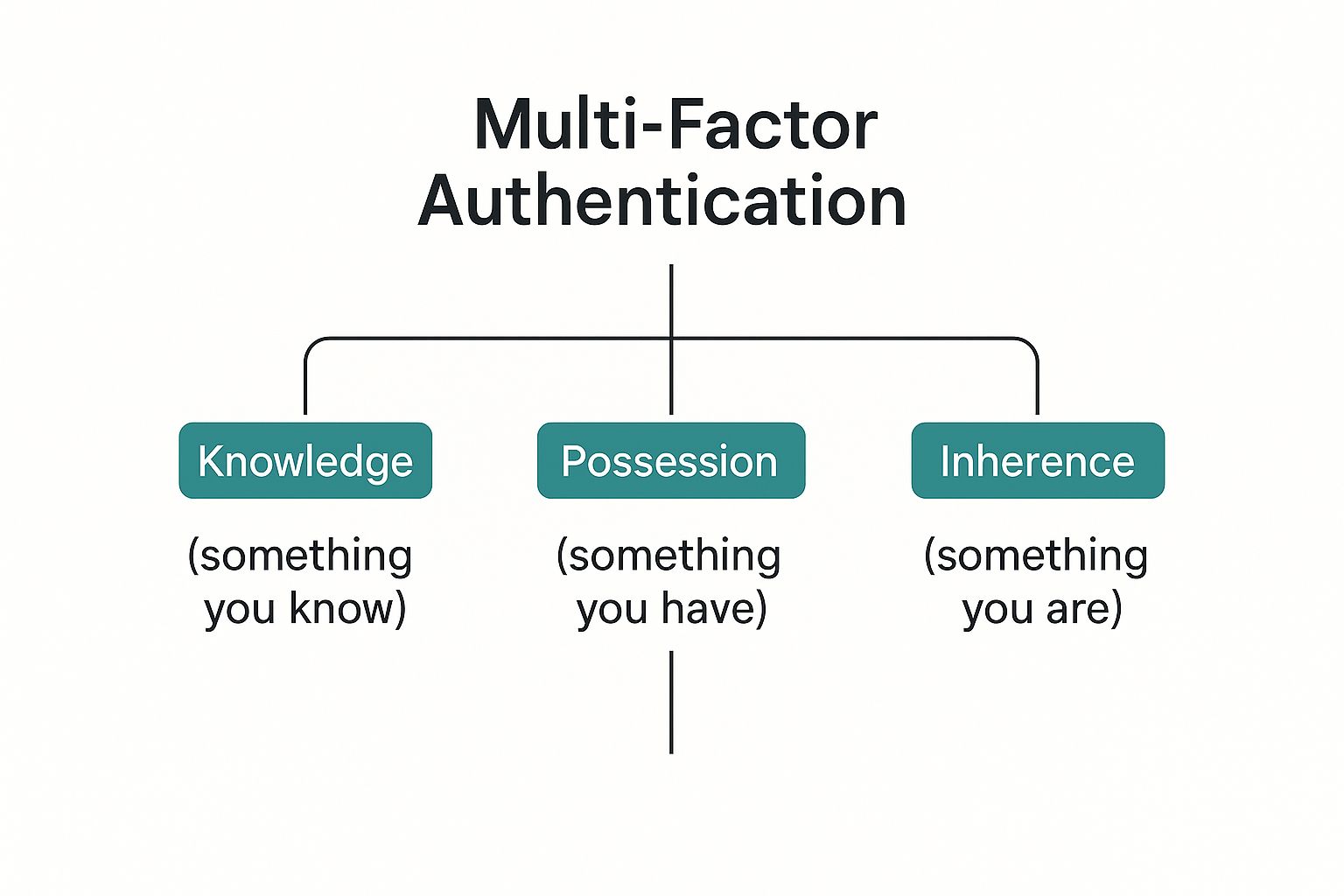
The Three Pillars of Authentication
At its core, MFA works by combining different types of credentials, or "factors," to verify a user's identity. These factors fall into three fundamental categories. A truly strong defense is built by mixing and matching these different pillars.
Let's have a look at what these are:
| Factor Type | Description | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge Factor | Something only you know. | Password, PIN, answer to a security question. |
| Possession Factor | Something only you have. | Smartphone (for an app push notification or SMS code), physical security key, smart card. |
| Inherence Factor | Something only you are. | Fingerprint scan, facial recognition, voiceprint, retina scan. |
As you can see, robust security isn't about having one strong lock; it's about layering different types of protection. If a hacker manages to steal your password (the knowledge factor), they still can't get in without also having your phone (the possession factor) or your fingerprint (the inherence factor).
Modern authentication solutions, especially those integrated with top-tier network hardware from vendors like Cisco and Meraki, make this layering feel almost invisible to the end-user. For instance, a student on a university campus might log into the WiFi through a Captive Portal using their password (something they know) and then approve a push notification sent to their phone (something they have). It’s a smooth, simple, and secure process.
In a corporate BYOD setting, an employee using their personal laptop could connect via an IPSK or EasyPSK solution that combines their device's unique key with a fingerprint scan (something they are). This layered strategy ensures that even if one factor is compromised, your digital assets remain secure behind the other layers. It's simply the modern standard for intelligent, secure network access.
Exploring the Different Types of MFA
Now that we’ve covered the "why" behind multi-factor authentication, let's get into the "how." Think of all the different MFA methods as unique types of keys and locks. Some are as simple as a hotel key card, while others are more like a high-tech retinal scanner from a spy movie. They all serve the same purpose: keeping your digital spaces locked down.
Figuring out which options are right for you is crucial, whether you're securing a busy Retail store or an entire university campus in the Education sector.
Possession Factors: "Something You Have"
This category is all about proving your identity with a physical or digital item you actually have on you. This is a powerful security layer because it's tough for a hacker on the other side of the world to steal something from your pocket or phone.
- SMS and Email Codes: This is the most straightforward method. You get a temporary code sent to your phone or email to finish logging in. It's super convenient, but it does have a weakness—if your phone or email account gets hacked, the code can be intercepted.
- Authenticator Apps: These are mobile apps that generate a new time-based one-time password (TOTP) every 30 seconds or so. It's a big step up in security from SMS because the code is created right on your device, not sent over a network.
- Hardware Tokens: These are small, physical devices, often resembling a key fob, that display a new code every 30 to 60 seconds. They offer fantastic security because they are completely disconnected from your computer or phone.
Inherence Factors: "Something You Are"
This is where security gets truly personal. Inherence factors use your unique biological traits, which are incredibly difficult for anyone to fake. You literally are the key.
Biometrics are popping up everywhere, especially in corporate BYOD sectors and on our personal devices. Think about the fingerprint scanner on your laptop or the facial recognition on your smartphone. These methods deliver a killer combination of high security and pure convenience. Just a touch or a glance, and you're in.
Interestingly, even though biometrics offer top-tier security, real-world data shows that a vast majority of employees using MFA still lean towards software-based methods like mobile apps. It’s a great reminder that convenience often plays a huge role in which tools people actually adopt.
Finding the Right Balance Between Security and Usability
Choosing the right MFA methods is always a balancing act. For example, in an Education setting, a student logging into the Wi-Fi through a Captive Portal could use their password plus a code from an authenticator app. That's a solid mix of security and ease of use.
On the other hand, for a sensitive corporate network running on Cisco Meraki hardware, you might want something more robust. Combining an IPSK or EasyPSK key with a biometric scan provides some seriously tough, layered protection.
If you're looking for a deeper dive into how specific tools integrate, you might find our guide on Duo multi-factor authentication helpful. At the end of the day, the best setup comes down to your specific security risks and how smooth the experience needs to be for your users.
Why Your Organization Needs MFA Right Now
Let's move past the theory and talk about the real world. This is where the case for multi-factor authentication becomes undeniable. MFA isn't just another "nice-to-have" security feature; it's an essential shield for any modern organization. It dramatically cuts down the risk of data breaches that start with stolen or weak passwords—which are still the number one way attackers get a foot in the door.
Just stop and think about the sheer volume of sensitive data your organization manages every single day. For an Education institution, that means student records and proprietary research. In Retail, it’s a treasure trove of customer payment information. In a corporate environment, it's the company's most valuable secrets. A single compromised password can put all of that on the line.
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) puts it bluntly: implementing MFA makes users 99% less likely to be hacked. That's a staggering statistic. This one step nearly wipes out the threat of credential theft, one of the most common and damaging cyberattacks out there.
Protecting Your People and Data Everywhere
The need for solid authentication solutions has exploded with the shift to remote work and Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies. The old idea of a secure network perimeter—the four walls of your office—is gone. Your perimeter is now every employee's home office, every student's dorm room, and every coffee shop where a team member decides to log on.
This is where MFA really proves its worth, especially when you pair it with powerful networking hardware from providers like Cisco Meraki. Consider these everyday situations:
- Education: A university can use a Captive Portal with MFA to make sure only registered students and faculty get onto the campus Wi-Fi, keeping academic systems safe.
- Retail: A chain of stores can completely separate its public guest Wi-Fi from the point-of-sale system by requiring MFA for all employee logins, effectively shutting the door on unauthorized access.
- Corporate BYOD: An employee brings their personal laptop to work. They connect to the company network using an IPSK or EasyPSK key, which then prompts for a second verification factor on their phone. Just like that, the connection is confirmed and secure.
By adding these simple layers, you're not just protecting data. You're building trust with your users and customers, all while satisfying increasingly tough data protection and compliance rules.
To take it a step further, you can learn more about locking down these connections in our guide on using security keys for WiFi, which adds a physical layer of defense.
In the end, putting MFA in place allows you to focus on what you do best—educating students, serving customers, or growing your business—without constantly worrying about the next cyber threat. It's one of the most fundamental steps you can take in modern digital security.
Putting MFA to Work with Cisco Meraki
Knowing what multi-factor authentication is in theory is one thing. Seeing it work in a real network is where you truly understand its power. This is exactly where an integrated solution like Cisco Meraki comes in, bridging the gap between a concept and a genuinely secure, yet simple, user experience.
The entire Meraki platform is built around cloud management, which makes layering MFA into your WiFi access a surprisingly straightforward process. You can protect your network without frustrating users who just want to connect quickly—a crucial balance for busy places like Retail stores or school campuses in the Education sector.
Modern Authentication in the Real World
A huge part of this is ditching the old-school, single WiFi password that everyone shares. That’s a security nightmare waiting to happen. Instead, modern approaches like IPSK (Identity Pre-Shared Keys) and EasyPSK are changing the game. Rather than one password for the entire "Guest" network, every single user or device gets its own unique key.
That alone is a massive security upgrade.
But now, imagine adding MFA on top of that. A user connects with their unique key (something they have) and is immediately asked to verify who they are with a push notification to their phone (another thing they have) or a quick fingerprint scan (something they are).
This is how you build a defense that has both depth and flexibility. The Cisco Meraki dashboard gives you a single pane of glass to manage all of this.
This kind of centralized view lets IT admins get really specific about who can access what, making it simple to roll out different security rules for different groups of people.
Tailoring Security to Your Environment
The real magic of a modern authentication setup is how it can adapt. A hospital has very different security needs than a coffee shop, so a one-size-fits-all approach is a non-starter.
- In Education: Think about a university campus. They can use a Captive Portal to get thousands of students online securely. When a student connects, the portal asks for their school login and an MFA code, guaranteeing only authorized people get to the academic network.
- In Retail: A department store might use that same Captive Portal for its guest WiFi. But for employees connecting to the point-of-sale network? That requires a much tougher policy using EasyPSK and a mandatory push notification to protect customer payment data.
- For Corporate BYOD: In an office where everyone brings their own laptop and phone, security is everything. A Cisco Meraki network can use IPSK to ensure only company-registered devices can even join the network, and then they still have to pass an MFA challenge to get to internal files.
This idea of layering security is a foundational principle of modern cybersecurity. It’s built on the assumption that no user or device should be trusted by default. This philosophy is the heart of a Zero Trust security model, where every single access request is verified, no matter where it comes from.
By bringing these powerful tools together, organizations can finally get a real handle on network access. If you want to dive deeper into this security mindset, our guide on what is Zero Trust security is a great place to start. It’s all about creating a smarter, more responsive security system that truly protects what matters most.
Seeing MFA in Action: Real-World Scenarios
The best way to get your head around the power of multi-factor authentication is to see how it works on the ground. This isn't just some abstract theory; it's a practical, everyday tool that organizations in Education, Retail, and Corporate sectors rely on to protect their most sensitive assets.
Let's walk through a few different environments to see how MFA, combined with the right authentication solutions, delivers security that's built for specific needs.
In Education: Securing Student Access
Picture a busy university campus. Thousands of students need seamless WiFi for everything from downloading lecture slides to submitting last-minute assignments. At the same time, the network is a treasure trove of sensitive data. How do you protect it all without making life difficult for users?
This is the perfect job for a solution like IPSK (Individual Pre-Shared Key) or EasyPSK. Instead of one shared password that could be leaked in minutes, each student gets their own unique WiFi key. The first time they connect a new device, a Captive Portal pops up. They enter their key and then approve a second factor, maybe a quick push notification sent to the official university app on their phone.
It's a simple, elegant solution. This one-two punch ensures only enrolled students get on the network, effectively walling off personal data and academic resources from prying eyes.
In Retail: Protecting Customer and Company Data
Now, let's head to a large retail chain. Every store has a public WiFi network for shoppers and a separate, locked-down network for point-of-sale systems. The nightmare scenario? A breach that exposes customer credit card numbers.
A network powered by a platform like Cisco Meraki can create a clean, strong separation between these two worlds. When an employee connects to the secure corporate network, they're met with a Captive Portal that demands MFA verification. This single step is a powerful defense, stopping an attacker dead in their tracks even if they've managed to steal an employee's password.
Meanwhile, shoppers get a friendly splash page for the guest network. For any business in the Retail sector, a well-managed guest WiFi is a fundamental part of protecting both your customers and your back-office operations.
In the Office: Enabling a Secure BYOD Culture
Finally, think about a modern office that embraces a "Bring Your Own Device" (BYOD) policy. People are using their personal phones, tablets, and laptops to access company resources. This boosts productivity, but it's a huge security headache. How do you keep company data safe on devices you don't even own?
MFA is the answer. When an employee connects their personal smartphone to the corporate WiFi using an IPSK or EasyPSK key, the system first checks if the device is registered. Then, it prompts for MFA. So, even if that phone is lost or stolen, a thief can't just waltz into the company's confidential files—they'd still need to get past that second authentication step.
This strategy allows companies to get all the benefits of BYOD without giving up control over their critical information. It’s this growing need for smarter security that has driven the global MFA market to a value of USD 10.3 billion, and you can dig deeper into that expansion with this market growth analysis.
Answering Your Common MFA Questions
As you look into adding multi-factor authentication to your organization, you're bound to have some questions. It's a big step up in security, and you need to know it’s the right move for both your users and your network. Let's walk through some of the most frequent questions to clear things up.
Is MFA a Hassle for Users?
That’s probably the most common concern we hear! While MFA does add a step to the login process, modern systems are designed to be as painless as possible. Often, it's as simple as a push notification where you just tap "Approve" on your phone—quick, easy, and intuitive.
Solutions from providers like Cisco Meraki even use what’s called adaptive MFA. This approach intelligently dials back how often users are prompted, especially if they’re on a trusted device or connecting from a known, safe location. That small initial adjustment is a tiny price to pay for such a huge leap in security.
For places like Retail stores or Education campuses, streamlined MFA on a Captive Portal can make the whole process nearly invisible to users while keeping the network locked down. The goal is always to find that sweet spot between robust security and a smooth user experience.
What’s the Real Difference Between 2FA and MFA?
This is a great question because the terms are often tossed around as if they mean the same thing. Here’s a simple, friendly way to think about it: all squares are rectangles, but not all rectangles are squares.
It's the same with authentication:
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) specifically means using exactly two different verification factors. A classic example is your password combined with an SMS code sent to your phone.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is the umbrella term for using two or more factors.
So, a high-security setup that requires a password, a physical hardware token, and a fingerprint scan is definitely MFA, but it goes beyond the strict "two-factor" definition of 2FA.
How Do I Get Started with MFA for My Business?
Getting the ball rolling is much simpler than you might think, particularly with today's integrated authentication solutions. The first thing you need to do is identify your most critical assets. Which user accounts, applications, and data absolutely cannot be compromised? Start there.
From that point, you can explore the authentication options built right into your network dashboard, like the tools offered by Cisco Meraki, to set up policies that demand MFA. You can apply these rules for WiFi access, VPN connections, or specific apps. With support for modern methods like RADIUS, IPSK, and EasyPSK, it's straightforward to roll out strong, layered security across your school, store, or office.
Can MFA Really Stop All Cyberattacks?
While MFA is incredibly powerful, it's crucial to view it as one layer in a comprehensive security strategy. No single tool can be a 100% silver bullet against every possible threat. What MFA does, however, is completely shut down the most common attack vector: stolen passwords.
By implementing MFA, you make compromised credentials almost useless to an attacker. Even if a hacker has a valid password, they are stopped cold without the second factor.
The proof is in the numbers. When one major tech company rolled out mandatory two-factor authentication, it resulted in a stunning 50% reduction in compromised accounts.
When you pair MFA with other best practices like network monitoring and user education, you build a formidable, layered defense that makes your organization a much harder target. For example, understanding how a WiFi Captive Portal works is another key piece in controlling who gets on your network in the first place.
Ready to build a stronger, more secure network for your users? Splash Access provides an instantly deployable platform that integrates seamlessly with Cisco Meraki to deliver secure, customizable, and user-friendly authentication experiences. Learn more at https://www.splashaccess.com.